2.3: Additional Programming Techniques
Exam Board:
OCR
Specification:
J277
This section of the specification includes programming topics that are outlined in 1.2 (Designing Algorithms). You must have an understanding of more complex programming techniques, such as how to manipulate strings, handle files and use subprograms. The best practice for learning is to try the tasks in the Python pages on this website (see the link to the right).
Subprograms
What is a subprogram?
Large programs are often broken down into smaller subprograms (also called subroutines). Each subprogram focuses on a specific function of the code, helping to decompose a complex problem into more manageable chunks.
Defining subprograms
A subprogram is defined (identified) using the def command in Python. A program may use many subprograms, which are usually defined at the start of the code.
Calling subprograms
Running a line of code that includes the name of a subprogram will call (activate) it. When called, the program will run the subprogram code before returning back to the line that called it. Subprograms are only run when called, so depending on decisions made, a program may end without calling every (or any) subroutine.
Parameters
A parameter is a value that is passed into a subprogram when it is called, allowing the value to be used within the subprogram. A subprogram may not use a parameter, e.g. multiply(), or one parameter, e.g. multiply(num), or several e.g. multiply(num1,num2). Any parameters must be identified when the subprogram is defined, e.g. def multiply(num):
Return
The return command will send a value back to the line the subprogram was called on, allowing it to be used there. For example, the 'quad' subprogram in the example below returns the value of the 'result' variable back to the main program, allowing it to be printed. A subprogram will end either by reaching the last line of code within it, or when it reaches a return command. Subprograms that return a value are called functions.

Subprogram example
This subprogram is defined using the identifier 'quad' with a parameter named number.
The subprogram is called in the main program, multiplies the number passed in as a parameter by 4 and returns a value back to the main program to be printed.
def quad(number):
result = number * 4
return result
#Main Program
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
print("The number quadrupled is" , quad(number))
Enter a number: 5
The number quadrupled is 20
Functions and Procedures
There are two types of subprograms.
A function is a subprogram that returns a value, using the return command, which allows the value to be used in the line of code the function was called in. The 'divide' function below returns the value of the variable 'total' to the main program to be printed.
A procedure is a subprogram that does not return a value.
Example of a Procedure
def multiply(num):
total = num * 2
print("The number doubled is" , total)
#Main Program
num = int(input("Enter a number: "))
multiply(num)
Enter a number: 4
The number doubled is 8
Example of a Function
def divide(num):
total = num / 2
return total
#Main Program
num = int(input("Enter a number: "))
print("The number halved is" , divide(num))
Enter a number: 9
The number halved is 4.5
Advantages of using subprograms

Subprograms break a complex program down into smaller parts, making it easier to design and test. Each subroutine can be tested separately and abstraction can be used to simplify a complicated problem.
Using subprograms allows code to be easily reused in other programs, as it has already been written, making it quicker to develop new programs or build on existing work.
Using subprograms avoids code repetition, as they can be called as many times as necessary. This makes programs shorter and quicker to develop, making them easier to maintain and debug.
Work can easily be split up between team members to work on different subprograms at the same time.
Array
An array is a static data structure that can hold a fixed number of data elements. Each data element must be of the same data type i.e. real, integer, string.
The elements in an array are identified by a number that indicates their position in the array. This number is known as the index. The first element in an array always has an index of 0.
You should know how to write pseudocode that manipulates arrays to traverse, add, remove and search for data. The following steps use Python as an example, although Python does not use arrays and uses a similar data structure called a list (that can change in size as the program runs). See the 8a and 8b Python pages for tasks on how to use lists.

What
Traversing an Array
To traverse ('move through') an array a for loop can be used to display each data element in order.
Example code for traversing:


Output:
'Inserting' a value
In an array the size is fixed so you cannot insert new values, but you can change the value of elements that already exist. Overwriting the fourth element (Daphne) with a new value (Laura) will change it from Daphne to Laura.
Example code for inserting:
Output:

'Deleting' a value
In an array the size is fixed so you cannot delete values, but you can overwrite them as blank. Overwriting the second element (Shaggy) with a blank space makes it appear deleted.
Example code for deleting:
Output:

Searching an Array
For large arrays a for loop is needed to search through each element for a specific value. This example checks each name to see if it is equal to Velma.
Example code for searching:

Output:
Two-Dimensional Array
Often the data we want to process comes in the form of a table. The data in a two dimensional array must still all be of the same data type, but can have multiple rows and columns.
The two-dimensional array to the right shows the characters from Scooby Doo along with their associated colour and their species.
Each value in the array is represented by an index still, but now the index has two values. For example [3] [0] is 'Daphne'. Unless stated in an exam, measure row first, then column.
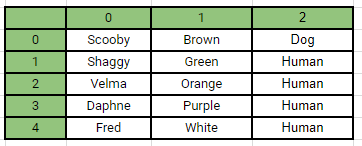

Searching a two-dimensional array:
To print a specific data element you can just use the index number like Daphne above. To search for a specific value you will need two for loops, one for the row and another for the values of each row.
The example to the right is looking for the value of 'Velma' and when it is found it prints the associated data from the whole row.
Example code for printing:
Output:
Example code for searching:

Output:
Records
Unlike arrays, records can store data of different data types.
Each record is made up of information about one person or thing.
Each piece of information in the record is called a field (each row name).
Records should have a key field - this is unique data that identifies each record. For example Student ID is a good key field for a record on students as no two students can have the same Student ID.
A 2D array may be used to represent database tables of records and fields.
SQL
SQL (structured query language) is a language that can be used to search for data in a database.
The format of an SQL statement is:
SELECT field1, field2, field3…
FROM table
WHERE criteria
Example of an SQL statement using the Cars table:
SELECT Make, Colour
FROM Cars
WHERE Miles > 1000 AND Age > 8
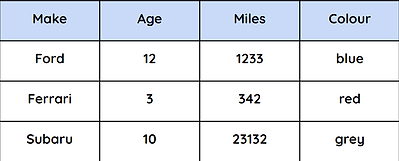
Cars table
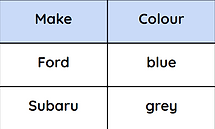
SQL uses wildcards which are symbols used to substitute characters.
The * symbol represents ALL fields.
Example:
SELECT *
FROM Cars
WHERE Colour = “blue”

Click the banner above to try a self-marking quiz (Google Form) on this topic.
Questo's Questions
2.3a - Additional Programming Techniques:
1a. Describe what the following terms mean: subprogram, parameter, function, procedure. [2 each]
1b. Describe three advantages of using subprograms. [6]
2. Describe the differences between a 1D array, 2D array and record. [3]
3. A one-dimensional array looks like this: TigerBreeds("Sumatran","Indian","Malayan,"Amur")
Write the code to:
-
a. Print the element with the index of 3. [2]
-
b. Change Indian to South China. [2]
-
c. Remove the Amur element. [2]
-
d. Search through the array for 'Malayan'. [2]
4a. Use the Cars table above to write the SQL statement to display the make and miles for cars that are grey OR blue. [3]
4b. Write an SQL statement to display all fields for cars that are 10 years old or less. [3]
